Expansion of a Product of Binomials
Here we look at two ways to approach the expansion or removal
of brackets from a product of the form
(5x + 3)(7x – 2)
in which two binomials are being multiplied together.
Method 1:
This is the “recipe method” based on the acronym
FOIL. The result of the multiplication is the sum of four terms:
| |
F(irst) – the product of the two
first terms in each binomial |
| plus |
|
| |
O(uter) – the product of the two
outer terms when viewed as shown above |
| plus |
|
| |
I(nner) – the product of the two
inner terms when viewed as shown above |
| plus |
|
| |
L(ast) – the product of the two last
terms in each binomial. |
Diagrammatically, using the example above, we have
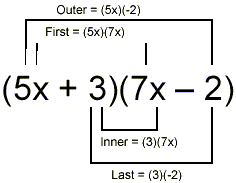
Then
(5x + 3)(7x – 2) = First + Outer + Inner + Last
= (5x)(7x) + (5x)(-2) + (3)(7x) + (3)(-2)
= 35x 2 – 10x + 21x – 6
= 35x 2 + 11x – 6
Notice that subtracts are handled as minus signs retained with
the terms being multiplied. At the end of the process, we also
carry out any simplification by collection of like terms that may
be obvious.
Example 1:
Expand (3x – 2y) (4x + 7y) .
solution:
(3x – 2y) (4x + 7y) = First + Outer + Inner + Last
= (3x)(4x) + (3x)(7y) + (-2y)(4x) + (-2y)(7y)
= 12x 2 + 21xy – 8xy – 14y 2
= 12x 2 + 13xy – 14y 2
Method 2:
This method exploits the definition of brackets and the
distributive law of multiplication. In the simpler problem of
expanding and expression such as
5x(7x – 2)
the ‘5x’ multiplying onto the bracketed expression
indicates that every term inside the brackets is to be multiplied
by 5x:
5x(7x – 2) = (5x)(7x) + (5x)(-2)
= 35x 2 – 10x
We just extend this notion to include multiplication by a
binomial instead of just a monomial. So
(5x + 3)(7x – 2)
means “multiply every term in (7x – 2) by the factor
(5x + 3).” This gives
(5x + 3)(7x – 2) = (5x + 3)(7x) + (5x + 3)(-2)
= 7x(5x + 3) - 2(5x + 3)
In the second line here, we’ve just rearranged the
previous expression slightly to remove some of the clutter. But
now you see that the original problem of expanding a product of
two binomials has turned into a problem of expanding two products
of a monomial and a binomial – the sort of thing that can be
handled by the procedures described in the previous note. So, we
just continue the multiplication process, making sure the final
result is simplified as much as possible. As usual, we handled
subtractions as additions of negated quantities. The overall
process in this example is:
(5x + 3)(7x – 2) = (5x + 3)(7x) + (5x + 3)(-2)
= (7x)(5x + 3) + (-2)(5x + 3)
= (7x)(5x) + (7x)(3) + (-2)(5x) + (-2)(3)
= 35x 2 + 21x – 10x – 6
= 35x 2 +11x - 6
identical to the result obtained with Method 1 earlier.
Example 2:
Expand (3x – 2y)(4x + 7y) .
solution:
We’ll demonstrate Method 2 for this problem:
(3x – 2y)(4x + 7y) = (3x – 2y)(4x) + (3x –
2y)(7y)
= (4x)(3x – 2y) + (7y)(3x – 2y)
= (4x)(3x) + (4x)(-2y) + (7y)(3x) + (7y)(-2y)
= 12x 2 – 8xy + 21xy – 14y 2
= 12x 2 + 13xy – 14y 2 .
|